Computer Vision Applications: Unlock Insights from Visual Data with AI
Computer Vision Applications: Unlocking the Power of Visual Data with AI
In today's data-driven world, visual information plays an increasingly dominant role. From the photos and videos we share online to the complex imagery captured by industrial sensors and medical devices, the volume of visual data is exploding. Computer vision applications are the key to making sense of this deluge, empowering artificial intelligence (AI) to understand, interpret, and act upon visual input. This technology allows machines to "see" and process images and videos much like humans do, but with greater speed, accuracy, and scalability.
By leveraging sophisticated algorithms and machine learning models, computer vision systems can identify objects, recognize faces, analyze scenes, and even predict future events based on visual cues. The implications are profound, transforming industries ranging from healthcare and retail to manufacturing and transportation. This article delves into the diverse and impactful world of computer vision applications, showcasing how AI is unlocking unprecedented insights from visual data.
Key Points:
- AI-Powered Understanding: Computer vision enables machines to interpret and understand visual information.
- Broad Industry Impact: Applications span healthcare, retail, manufacturing, security, and more.
- Data-Driven Insights: Visual data can be analyzed to derive actionable intelligence.
- Automation & Efficiency: Computer vision drives automation, improving operational efficiency.
- Future Potential: Emerging trends point to even more revolutionary uses of this technology.
The Pillars of Computer Vision: How AI Sees and Understands
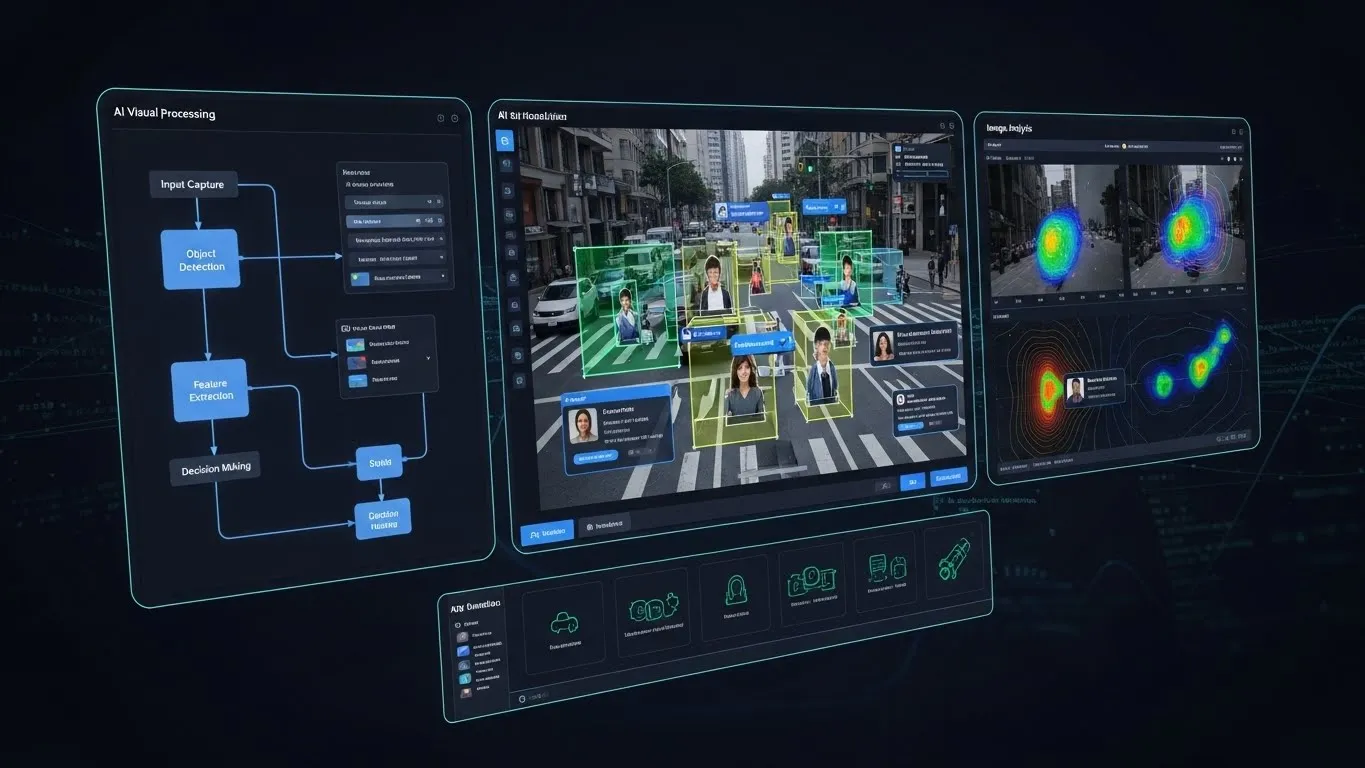
At its core, computer vision relies on AI to process and analyze digital images or videos. This process typically involves several key stages: image acquisition, image processing, feature extraction, object detection/recognition, and finally, interpretation or action. Machine learning, particularly deep learning with convolutional neural networks (CNNs), has revolutionized these stages, enabling AI models to learn complex patterns directly from raw pixel data.
- Image Acquisition: This is the initial step where visual data is captured, either through cameras, scanners, or other imaging devices.
- Image Preprocessing: Raw images often require cleaning and enhancement. Techniques like noise reduction, contrast adjustment, and image resizing are crucial for preparing the data for analysis.
- Feature Extraction: AI algorithms identify distinctive features within an image – edges, corners, textures, or specific shapes. Deep learning models automate this process, learning hierarchical features.
- Object Detection & Recognition: This is where the AI identifies what is in the image (recognition) and where it is located (detection). This could be as simple as identifying a cat or as complex as recognizing a specific type of faulty component on a production line.
- Scene Understanding: Beyond individual objects, advanced computer vision can understand the context and relationships between elements within an image or video, comprehending the overall scene.
The continuous advancements in AI, especially in deep learning, have dramatically improved the accuracy and capabilities of computer vision systems. This has opened the door to a vast array of practical applications that were once the realm of science fiction.
Transformative Computer Vision Applications Across Industries
The versatility of computer vision means its applications are almost limitless. Here, we explore some of the most impactful areas where AI is making a significant difference.
Healthcare: Enhancing Diagnostics and Patient Care
In healthcare, computer vision applications are revolutionizing how diseases are diagnosed and treated. AI-powered tools can analyze medical images with incredible precision, often detecting subtle anomalies that might be missed by the human eye.
- Medical Image Analysis: AI algorithms analyze X-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and pathology slides to detect conditions like cancer, diabetic retinopathy, and cardiovascular diseases. For instance, a study published in Nature Medicine in 2023 highlighted AI's ability to accurately detect breast cancer from mammograms, often outperforming radiologists in early detection.
- Surgical Assistance: Computer vision systems can guide surgeons during procedures, providing real-time visual feedback, identifying critical anatomical structures, and improving precision.
- Drug Discovery: Analyzing microscopic images of cells and tissues can accelerate the drug discovery process by identifying promising compounds and understanding their effects.
Retail: Revolutionizing the Customer Experience
The retail sector is leveraging computer vision to enhance customer engagement, optimize store operations, and personalize shopping experiences.
- Inventory Management: Cameras equipped with computer vision can monitor stock levels on shelves, automatically reordering items when they are low and reducing instances of stockouts. This can significantly improve efficiency and reduce lost sales.
- Customer Behavior Analysis: By analyzing anonymized video footage, retailers can understand customer traffic patterns, popular product displays, and dwell times, informing store layout and merchandising strategies. A report from Forrester in late 2024 indicated a 15% increase in conversion rates for retailers implementing such insights.
- Checkout-Free Stores: Technologies like those pioneered by Amazon Go use computer vision to track items customers pick up, allowing them to leave the store without traditional checkout lines.
Manufacturing and Industrial Automation: Improving Quality and Efficiency
In manufacturing, computer vision is a cornerstone of modern automation, driving quality control, process optimization, and worker safety.
- Quality Control and Defect Detection: High-speed cameras and AI can inspect products on assembly lines for defects, ensuring consistent quality and minimizing waste. This is critical in industries where even minor flaws can have significant consequences.
- Robotics and Automation: Computer vision enables robots to "see" and interact with their environment, performing complex tasks like pick-and-place operations, assembly, and welding with greater accuracy.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing visual data from machinery (e.g., wear and tear on components), AI can predict potential failures before they occur, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
Automotive and Transportation: Enhancing Safety and Autonomy
The automotive industry is perhaps one of the most visible beneficiaries of computer vision, particularly in the pursuit of autonomous driving.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Computer vision is essential for self-driving cars to perceive their surroundings, detect pedestrians, other vehicles, traffic signs, and road boundaries. This allows them to navigate safely and make real-time driving decisions.
- Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS): Features like lane departure warnings, automatic emergency braking, and adaptive cruise control all rely on computer vision to monitor the vehicle's environment and assist the driver.
- Traffic Management: Computer vision can analyze traffic flow, detect congestion, and optimize traffic light timings, leading to smoother and more efficient transportation networks.
Security and Surveillance: Smarter Monitoring and Threat Detection
Computer vision is transforming security systems, moving beyond simple recording to intelligent threat detection and analysis.
- Facial Recognition: While controversial, facial recognition technology is used for access control, identifying individuals in crowds, and enhancing security protocols.
- Anomaly Detection: AI can monitor surveillance feeds to identify unusual activities, such as unauthorized access to restricted areas, abandoned packages, or loitering, alerting security personnel in real-time.
- Crowd Analysis: In public spaces, computer vision can monitor crowd density and movement to prevent overcrowding and ensure public safety.
Emerging Trends and Differentiated Value in Computer Vision
The field of computer vision is not static; it is constantly evolving with groundbreaking research and development.
One key differentiator and emerging trend is the increasing focus on explainable AI (XAI) in computer vision. As these systems become more integrated into critical decision-making processes, understanding why an AI made a particular decision is paramount. Researchers are developing methods to provide transparency into the decision-making process of complex deep learning models, building trust and allowing for better debugging and refinement. This is a critical step beyond simply achieving high accuracy.
Another significant development is the rise of edge AI for computer vision. Traditionally, complex computer vision tasks required powerful cloud servers. However, with advancements in hardware and model optimization, many computer vision applications can now run directly on devices like smartphones, drones, and IoT sensors. This "on-device" processing reduces latency, enhances privacy by keeping data local, and lowers reliance on constant internet connectivity. Imagine real-time object detection on a security camera without sending all video data to the cloud. This enables a new wave of responsive and privacy-conscious applications.
The Future is Visual: Continued Innovation in Computer Vision
The journey of computer vision applications is far from over. We are witnessing rapid progress in areas like:
- 3D Computer Vision: Moving beyond 2D images to understand depth and spatial relationships, crucial for robotics and augmented reality.
- Video Understanding: Developing AI that can not only identify objects in videos but also understand actions, events, and narratives over time.
- Generative AI for Visuals: Creating new, realistic images and videos, with applications in design, content creation, and synthetic data generation for training AI models.
The ability of AI to unlock insights from visual data is profoundly changing our world. As computer vision technology continues to mature, its integration into our daily lives and across industries will only deepen, offering new possibilities for innovation, efficiency, and understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions About Computer Vision Applications
Q1: What is the primary benefit of using computer vision in business? A1: The primary benefit is the ability to automate complex visual analysis tasks, leading to increased efficiency, accuracy, cost savings, and the extraction of valuable insights from visual data that would otherwise be overlooked.
Q2: How does computer vision differ from traditional image processing? A2: While traditional image processing focuses on manipulating pixels for enhancement or basic analysis, computer vision uses AI and machine learning to interpret the content of images, recognizing objects, scenes, and patterns to derive meaning and make decisions.
Q3: Is computer vision technology expensive to implement? A3: The cost varies greatly depending on the complexity of the application. While some advanced solutions require significant investment, many off-the-shelf tools and cloud-based services are making computer vision more accessible to businesses of all sizes.
Q4: What ethical considerations are associated with computer vision applications? A4: Ethical concerns primarily revolve around data privacy, potential biases in AI algorithms leading to unfair outcomes, and the responsible use of surveillance technologies like facial recognition. Ongoing research aims to address these challenges.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Computer vision applications are undeniably at the forefront of AI innovation, empowering us to extract actionable insights from the ever-increasing torrent of visual data. From revolutionizing healthcare diagnostics to optimizing retail operations and enabling autonomous vehicles, the impact is tangible and far-reaching. As this technology continues to evolve, with advancements in explainable AI and edge computing, its potential to reshape our future is immense.
We encourage you to explore how computer vision can benefit your specific industry or area of interest. Understanding these applications is the first step towards harnessing their power.
What are your thoughts on the future of computer vision? Share your insights in the comments below!
For readers interested in the broader landscape of AI and its applications, you might find articles on natural language processing techniques and machine learning model development to be particularly insightful. Understanding how different AI disciplines intersect is key to grasping the full potential of artificial intelligence.